Nov 5
2019
How Telehealth And eConsults Are Reducing Patient Wait Times
By Brooke LeVasseur, CEO, AristaMD.

The shortage of specialist physicians in the United States continues to receive a great deal of attention as an area of concern. However, a lesser-known compounding factor is the increase in referral rates. In a 2012 study, the National Ambulatory Medical Care Surveys found that between 1999 and 2009, the probability of receiving a specialist referral during an ambulatory patient visit increased from 4.8% to 9.3%, a 92% increase, nearly double. While this study is now several years old, we can surmise that this trend has continued due to the persistence of several factors contributing to the overall disparity between specialist referrals and the number of available specialist physicians.
The clear impact of these compounded problems is substantially increased wait times among patients with a physician referral for specialist appointment. In 15 major metro areas, a recent Merritt Hawkins study covering the medical specialties of cardiology, dermatology, orthopedic surgery, and obstetrics and gynecology, found appointment wait times increased 25% from 2014 to 2017. Wait times averaged 24.1 days across the study, with some extreme cases waiting 165 days for an appointment.
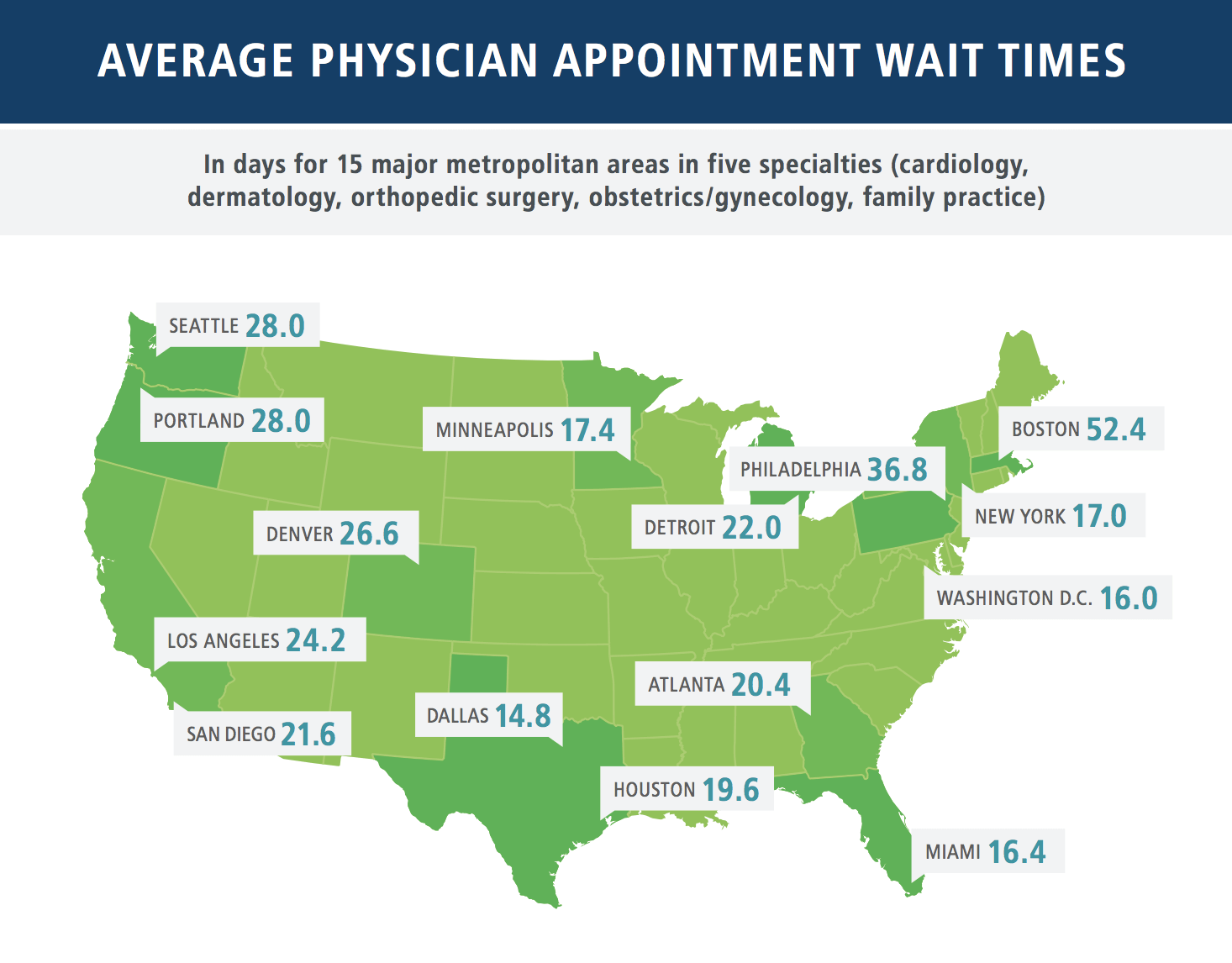
Image source: https://www.hospitalcouncil.org/sites/main/files/file-attachments/mha2017waittimesurvevy.pdf
Long wait times impact patient outcomes and healthcare operations
On top of the anguish and emotional impact of waiting for care, diseases and illnesses can progress as patients sit in appointment queues for weeks or even months on end. As NEJM describes, “long waits before appointments, particularly specialist appointments, often contribute to the development of avoidable complications,” which cause more difficult health cases both for the patient and for the physicians caring for them.
There are notable effects on healthcare operations that add to the case for reducing patient wait times as a crucial avenue for improving healthcare overall. For example, long wait times for appointments increase the prevalence of no-shows, indicating that patients are either frustrated enough to not follow through on scheduled appointments or forget appointments altogether because of the long interim period. Sometimes appointments can even be moved around by specialist physicians at the last minute, leaving patients in limbo for even longer.
Additionally, long wait times frequently lead to patients receiving inefficient care. Firstly, extended waits often deter patients from seeking initial care. This shifts the healthcare industry away from proactive to reactive care, which is less effective and more costly for all parties involved. Secondly, the inability to access the care they need and when they need it, leads to patients seeking care within inappropriate settings. These patients are more likely to be admitted to EDs, as the 30-day rate of ED and inpatient usage was 8.7 times higher for patients awaiting a specialist appointment. A study by Truven Health Analytics noted that 71% emergency room visits are unnecessary and avoidable. Each of these issues alone make strong cases for reducing patient wait times; these issues combined suggest reducing patient wait times is a crucial goal that must be prioritized when it comes to streamlining healthcare delivery and improving quality of care.
In light of these concerning figures and effects, healthcare organization operations are turning their focus toward reducing wait times and improving patient outcomes. This fits well as part of an overall strategy to increase quality and efficiency of healthcare delivery. Below, we will focus on how telehealth platforms, specifically eConsults, combat multiple factors driving specialist appointment wait times, streamlining the physician referral process and thereby reducing patient wait times for happier and healthier patients.
Positive impacts of reducing patient wait times by accessing specialty care from within primary care
Increasingly, healthcare providers are entering into value-based payment arrangements. Telehealth solutions, and specifically eConsults, can support the drive toward more efficient care by increasing access to specialists while better optimizing time and place of care.
eConsults are is an electronic form of peer-to-peer collaboration, providing PCPs with a platform to consult with specialists on specific patient cases. eConsult interaction occurs using a secure, HIPAA-compliant messaging platform, where specialist guidance is received within 24 hours, drastically reducing the interim time between referral and treatment. eConsults can replace more than 70% of routine referrals with immediate, specialist-guided treatment from the PCP, without the wait and additional cost. Keeping lower acuity patients out of the specialist referral queue means faster access to face-to-face visits for the higher acuity patients, expediting care and improving outcomes for all.
One provider (and frequent user of AristaMD eConsults) at a Federally Qualified Healthcare Center describes the challenges of securing specialty care for the patients at her clinic: “Especially with MediCal patients, it usually takes at least four or five months for a patient to complete a referral. Very often, patients end up waiting three to five months, then receive notification their appointment has changed, the specialist has moved, or even that the specialist is no longer taking that patient’s insurance. Some of these patients are then in limbo for more than six to nine months. This is where the benefit of AristaMD’s eConsult platform comes in. AristaMD specialists provide guidance on patient care plans, for example diagnostic or medication recommendations, within 24 hours.”
Several studies have already noted demonstrable decreases in wait times once eConsults were introduced in large health systems. The San Francisco Department of Public Health saw dramatic improvements following the introduction of their eConsult program. The median wait time for a non-urgent appointment with a rheumatology specialist was drastically reduced from 126 days to 29 days. Additionally, patients visiting specialists needed fewer follow-up appointments as a result of a more extensive pre-visit workup made possible by this telehealth platform. Other similar successes have been observed in Los Angeles and the NYC Health + Hospitals System, with the latter finding that median wait times for high-urgency specialist visits decreased from 30 days to 16 days as a result of eConsult implementation.
Conclusion
eConsults are ideal for addressing the growing problem of lengthy patient wait times. They empower PCPs to deliver specialist-guided care to lower acuity patients in a timely manner while freeing up the capacity for in-person specialist visits for the more complex, higher acuity patients who need them most.